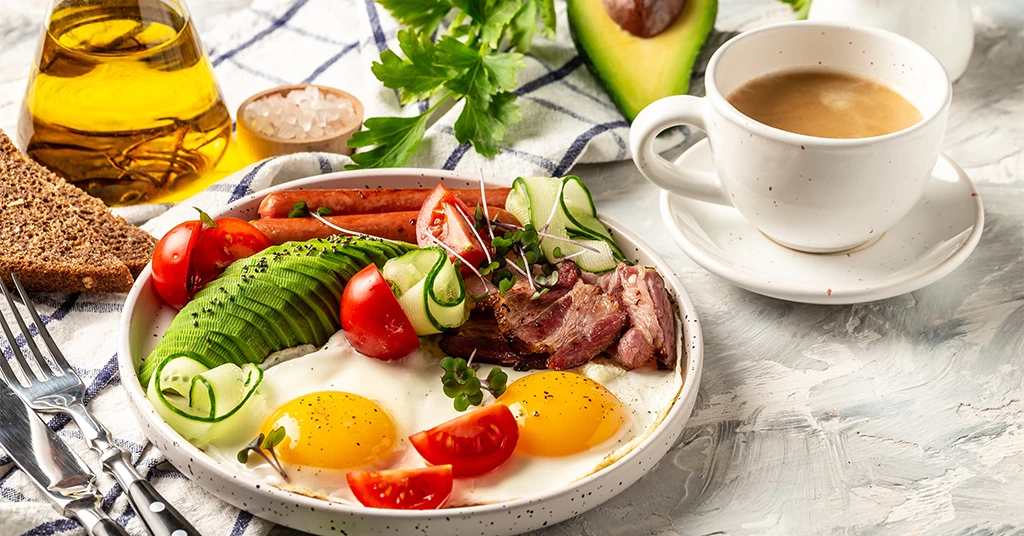
Eating a healthy lifestyle diet shouldn’t just be your New Year’s resolution. It should be incorporated long term throughout the year. Using food as fuel helps keep our bodies running efficiently and functioning at their best. Various lifestyle diets have gained popularity, each emphasizing unique nutritional benefits. Whether focused on weight management, health improvement, or ethical choices, understanding diets like Paleo, Keto, Veganism or Mediterranean diets can provide valuable insights into your food choices.
Think of food as the energy source that powers every cell in your body. Healthy lifestyle diets of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals are essential for various bodily functions. Each nutrient plays a unique role:
- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary source of quick energy, found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes.
- Proteins: Crucial for building and repairing tissues, found in meat, milk, beans, and nuts.
- Fats: Serve as a long-term energy reserve and aid in absorbing certain vitamins. Avocados, nuts, and olive oil are good sources of healthy fats.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential for various bodily functions.
Don’t know how to read a nutrition label? Learn More
Exploring Diets:
Many lifestyle diets concentrate on specific food groups or eating patterns. Here is a list of different diets and their benefits.
Paleo Diet
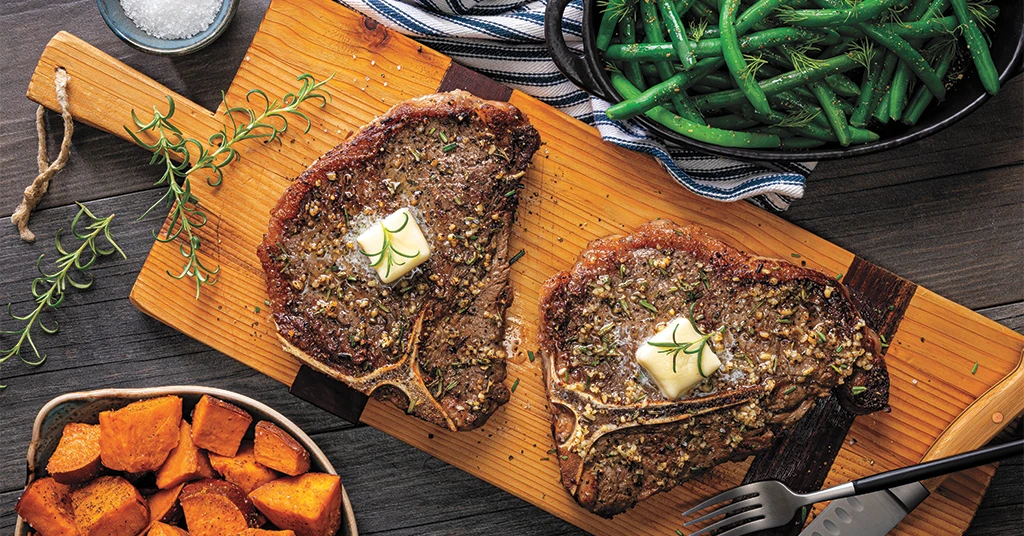

The Paleo diet is based on the common belief that by mimicking the eating habits of our hunter-gatherer ancestors, during the Paleolithic era, we can improve our health. The Paleo diet emphasizes consuming unprocessed, whole foods while discouraging the intake of packaged and processed foods. It includes lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, excluding processed foods, grains, and dairy. Benefits include weight loss, improved blood lipids, and better blood sugar control.
What You Can Eat on the Paleo Diet:
- Lean Proteins: Enjoy grass-fed meats, free-range poultry, wild-caught fish, and eggs from pasture-raised chickens as primary protein sources.
- Healthy Fats: Embrace healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, and nuts/seeds for energy and essential nutrients.
- Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Load your plate with colorful fruits and vegetables for vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Nuts and Seeds: Incorporate nuts (almonds, walnuts) and seeds (chia, flax) for healthy fats, proteins, and fiber.
- Limited Natural Sweeteners: Use natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup in moderation.
What to Avoid on the Paleo Diet:
- Processed Foods: Processed foods are not allowed because they often include refined sugars, artificial additives, and trans fats.
- Grains and Legumes: Avoid grains like wheat, barley because most of them are processed foods that our ancestors didn’t eat. Also avoid legumes such as beans and lentils because they are difficult to digest.
- Dairy Products: Exclude dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt due to potential inflammatory properties.
- Processed and Refined Oils: Steer clear of vegetable oils like soybean, corn, and canola oil, as they are refined, opting for natural fats instead.
- Highly Processed Sweeteners: Refrain from using highly processed sweeteners like high-fructose corn syrup or artificial sweeteners.
Shop for the Paleo Diet Here
Vegan Diet
A Vegan diet excludes all animal products and focuses on plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds. Some of the potential benefits include weight loss, lower risk of heart disease, and reduced environmental impact.
Vegan vs. Vegetarian:
Veganism and vegetarianism share similarities, but veganism is stricter. Vegetarians avoid animal flesh but often consume dairy and eggs. Vegans steer clear of all animal-derived foods, including products like honey.
Vegan Friendly Foods:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Load your plate with abundant colorful fruits and vegetables packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Embrace nutrient-dense whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, oats, and barley for sustained energy.
- Legumes and Pulses: Incorporate protein-rich legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and peas into your meals.
- Nuts and Seeds: Enjoy a variety of nuts (almonds, cashews) and seeds (chia, flax) for healthy fats and additional protein.
- Plant-based Dairy Alternatives: Explore dairy-free alternatives like coconut milk, oat milk, almond milk, soy milk and yogurt, and cashew cheese to replace animal-derived products.
What to Avoid on a Vegan Diet:
- Animal Products: Strictly eliminate animal-derived products like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and honey.
- Gelatin and Certain Additives: Watch out for products containing gelatin (often from animal sources) and some additives like certain food colorings (e.g., cochineal extract).
- Certain Baked Goods: Check for ingredients like eggs and dairy in baked goods like cakes, cookies, and pastries.
- Non-Vegan Sweeteners: Avoid honey and other non-vegan sweeteners commonly used in products as they are derived from animal sources.
Want to learn how to shop Vegan at the grocery store? Learn More
Shop Vegan Friendly Foods
Mediterranean Diet
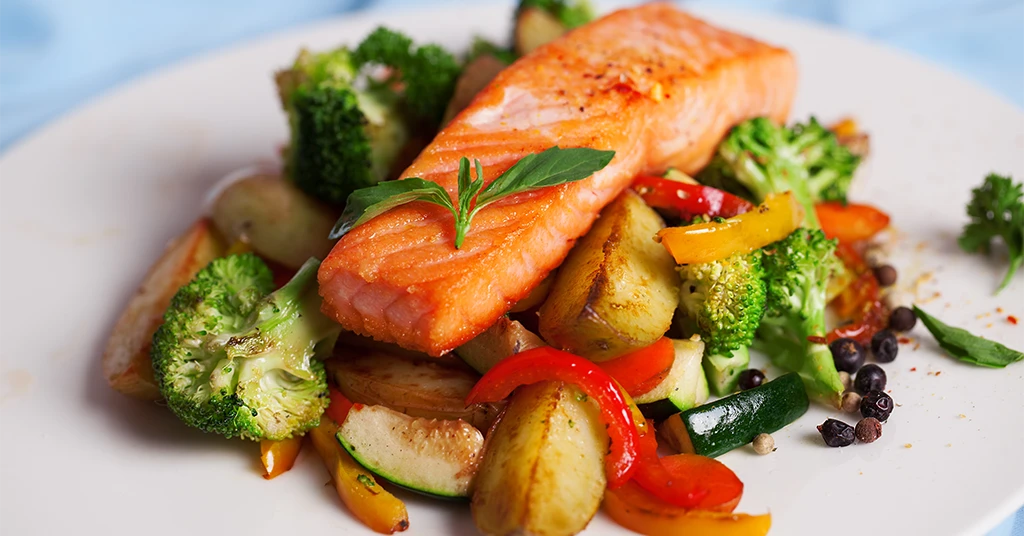

The Mediterranean Diet consists of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, fish, and healthy fats like olive oil. It’s associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, improved brain health, and longevity.
Mediterranean Friendly Foods:
- Abundance of Plant-Based Foods: Load your meals with fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds as the foundation of this diet.
- Healthy Fats: Embrace heart-healthy fats such as extra virgin olive oil, avocados, and nuts for their nutritional benefits.
- Lean Proteins: Include moderate amounts of poultry, fish, and seafood as primary protein sources.
- Dairy in Moderation: Consume moderate amounts of dairy, mainly Greek yogurt and cheese.
- Herbs and Spices: Flavor your dishes with herbs like basil, oregano, and thyme, and use spices such as cinnamon and cumin to enhance taste.
What to Limit or Avoid on a Mediterranean Diet:
- Red Meat and Processed Meats: Minimize intake of red meat and processed meats, focusing instead on leaner protein sources.
- Added Sugars and Sweets: Reduce consumption of added sugars, sugary beverages, and sweets to maintain balance.
- Refined Grains and Processed Foods: Limit processed foods and opt for whole grains over refined grains like white bread and pasta.
- Trans Fats and Unhealthy Oils: Limit the intake of unhealthy fats like margarine and refined vegetable oils.
- Excessive Salt: When cooking, choose natural flavors and herbs instead of excessive salt as it can cause high blood pressure and other serious health risks.
Shop for the Mediterranean Diet
Remember, food is the fuel that keeps our bodies functioning optimally. Whether it’s Paleo, Keto, Vegan, or Mediterranean, each diet offers unique benefits, but the key lies in finding what works best for you.
Consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help you navigate these diets and find the one that suits your lifestyle and health goals.
Resources:
Paleo Diet: Is It Another Fad? | The University of Vermont Health Network (uvmhealth.org)
Paleo diet: What is it and why is it so popular? – Mayo Clinic
Keto Diet – What Is The Keto Diet? | familydoctor.org
What is the Vegan Diet? – Food Insight









