Nutrition labels are the unsung heroes of our grocery shopping journeys, providing a wealth of information that can help us make informed decisions with our health. In this guide, we’ll delve into the basics of deciphering food nutrition labels, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed choices for a healthier lifestyle.
What is a Nutrition Label?
Ever glanced at the back of a food package and wondered what all those numbers and percentages mean? Nutrition labels serve as comprehensive guides, offering a detailed breakdown of a product’s nutritional content. These labels go beyond mere packaging; they provide vital information about the quantity of calories, essential nutrients, and potential allergens present in a food item.
Regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), nutrition labels are designed to ensure accuracy, consistency, and standardized information. This regulatory oversight guarantees that consumers receive reliable data, enabling them to make informed choices about their dietary intake.
The Role of the FDA in Regulating Labels
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing and regulating nutrition labels. By establishing and enforcing guidelines, the FDA ensures that labels are consistent across different products. This regulatory consistency simplifies the process for consumers to compare nutritional information when selecting items from the shelves.
Why it Matters: Making Informed Decisions for a Healthier Lifestyle
Understanding nutrition labels is not merely a matter of curiosity; it is a powerful tool for making informed decisions that directly impact our overall health and wellness. Armed with the knowledge gleaned from these labels, consumers can navigate the aisles of grocery stores with confidence, selecting products that align with their dietary goals.
In summary, breaking down nutrition labels becomes a key step in the journey toward a healthier and more mindful lifestyle.
Breakdown of a Nutrition Label
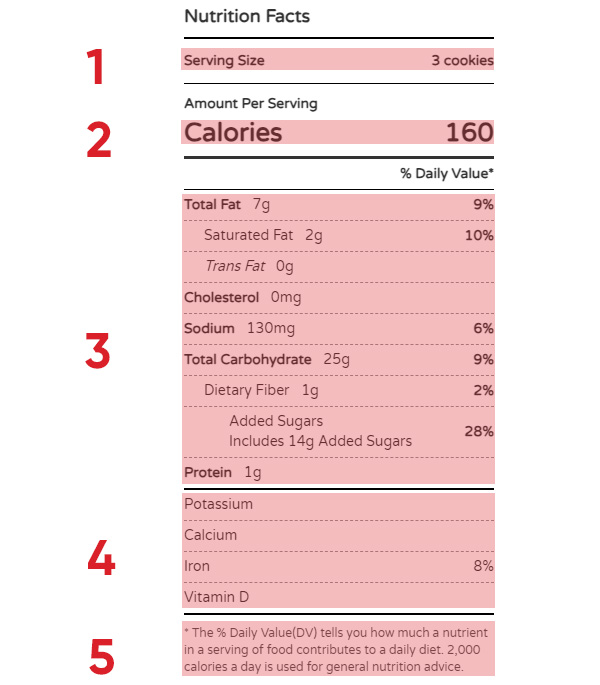
1. Serving Size
Serving size is the key to understanding the quantity of a product that the nutritional information refers to. Understanding what a serving is measured can help determine portions. Considering the serving size will help you to compare similar products.
2. Calories
The calorie count can help you determine quickly how much energy you’ll get from a serving of this food. Generally speaking, the recommended healthy intake of calories per day is 2,000. Being able to quickly identify how many calories are in a serving, can help you identify if it’s a good food choice.
3. Nutrient Content
Checking the nutrients in a serving size can also help determine if this food is a good choice for you. Just below the Calorie count, you’ll find a list of nutrients that are in the product, per serving size. Reading the nutrients provided in food can help manage your eating habits.
A. Macronutrients: Fueling the Body
- Proteins: Essential for the growth and repair of tissues and muscles, proteins are the body’s building blocks.
- Carbohydrates: Serving as the primary source of energy, carbohydrates fuel daily activities and maintain optimal brain function.
- Fats: Often misunderstood, fats play a vital role in absorbing nutrients and supporting overall cellular function.
Types of Fat includes:
- Saturated Fat: Found in animal products and certain oils, excessive consumption may contribute to heart issues.
- Trans Fat: Artificially created and known to increase the risk of heart disease; minimizing intake is advisable.
- Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fats: Considered heart-healthy, these fats are found in nuts, seeds, and certain oils.
4. Vitamins & Minerals
This is a list of potentially beneficial nutrients found in the food. Dietary Fiber, Iron, Calcium, Vitamin D, and Potassium are common nutrients to check for. These specific nutrients are good to incorporate into a healthy diet.
A. Micronutrients: The Powerhouses in Small Packages
Vitamins: These organic compounds are crucial for various bodily functions.
- Vitamin A: Can help promote for vision health, immune function, and skin health.
- B-Vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12): Supports metabolism, energy production, and nerve function.
- Vitamin C: Recognized for immune-boosting properties and collagen production.
- Vitamin D: Promotes bone health and aiding calcium absorption.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that can protect cells from damage.
Minerals: Essential for maintaining overall health.
- Calcium: Vital for strong bones and teeth.
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport in the blood.
- Potassium: Regulates blood pressure and supports muscle function.
- Magnesium: Involved in numerous of biochemical reactions in the body.
- Sodium: Important for fluid balance but excessive intake may contribute to high blood pressure.
Other Essential Components:
- Cholesterol: Present in animal-based foods, moderation is key to maintaining heart health.
- Dietary Fiber: Helps digestive health, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Sugar: While naturally occurring sugars in fruits are beneficial, added sugars should be limited to promote overall health.
5. Percent Daily Value (%DV)
This percentage represents how much of the nutrient you should include in your diet. Knowing this percentage will help you to determine if you’re meeting your daily nutrient intake.
As you embark on your nutritional journey armed with this newfound knowledge, let nutrition labels be your trusted companion. Consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized advice tailored to your specific health conditions and needs.
